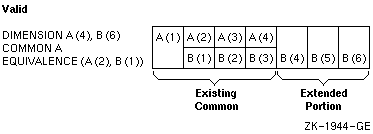
A common block can extend beyond its original boundaries if variables or arrays are associated with entities stored in the common block. However, a common block can only extend beyond its last element; the extended portion cannot precede the first element in the block.
Examples
Figure 5-3 and Figure 5-4 demonstrate valid and invalid extensions of the common block, respectively.
Figure 5-3 A Valid Extension of a Common Block

Figure 5-4 An Invalid Extension of a Common Block
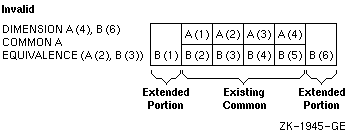
The second example is invalid because the extended portion, B(1), precedes the first element of the common block.
The following example shows a valid EQUIVALENCE statement and an invalid EQUIVALENCE statement in the context of a common block.
COMMON A, B, C
DIMENSION D(3)
EQUIVALENCE(B, D(1)) ! Valid, because common block is extended
! from the end.
COMMON A, B, C
DIMENSION D(3)
EQUIVALENCE(B, D(3)) ! Invalid, because D(1) would extend common
! block to precede A's location.